How accurate is your translation?
Certain documents may have specific translation or regulatory quality requirements. This type of translation is widely used when the accuracy of the language is particularly important. In financial investment, is 100% capital-secured the same as 100% capital guaranteed? How do you identify such issues during the translation process?
The objective of the process is to identify the following…
- review accuracy
- target reflects source
- translation accuracy
- differentiation from original text
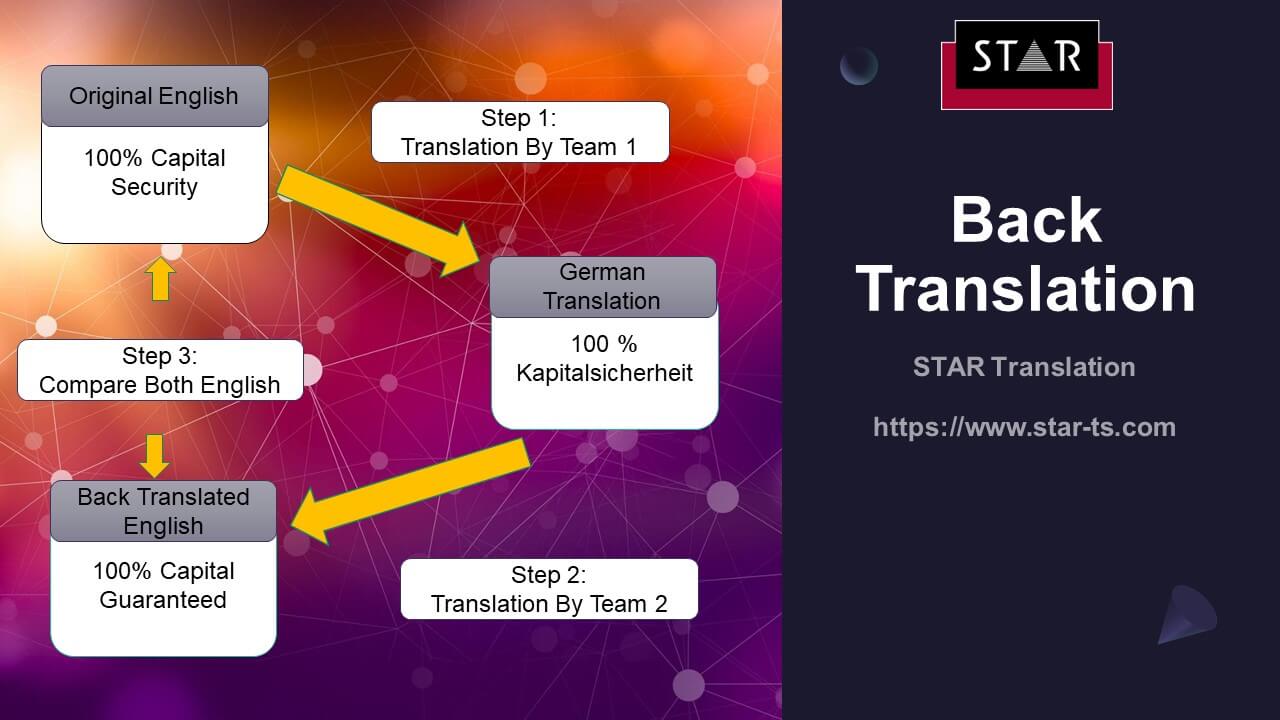
Best Practice for Back Translation
- Use Two Translation teams
Two completely autonomous teams work on your project. The first team translates into the target language, and the second translation team will translate the new language back into source language (frequently English) without reference.
- Compare Both Original Language Documents
Then both sets of source language documents (the original copy and the back translated document) are compared to see if they are the same. Wherever the translation differs from the original source (English), the translation is reviewed by first the back translation team to confirm the back translation is correct and then by the original translation team.
This is the best practice process to deliver the most accurate translation and to provide an independent audit trail.
Marketing and Back Translation
It can be used in marketing text translation. Often marketing copy can be emotional or have a specific message that sells to its audience. So when translated it becomes more than just about the words. Will the translation carry the same sales message, the same branding message, will it still be relevant to the target audience?
Performing back translation review can ensure that you compare the meanings as well. Once you are happy your meaning, intent and the brand is maintained, you know your translation quality is correct for your target market.